AI-based Computer Vision Tasks
Before we dive into instance segmentation, let’s start with a brief overview of different computer vision tasks so that we can understand the full implication of using instance segmentation techniques.
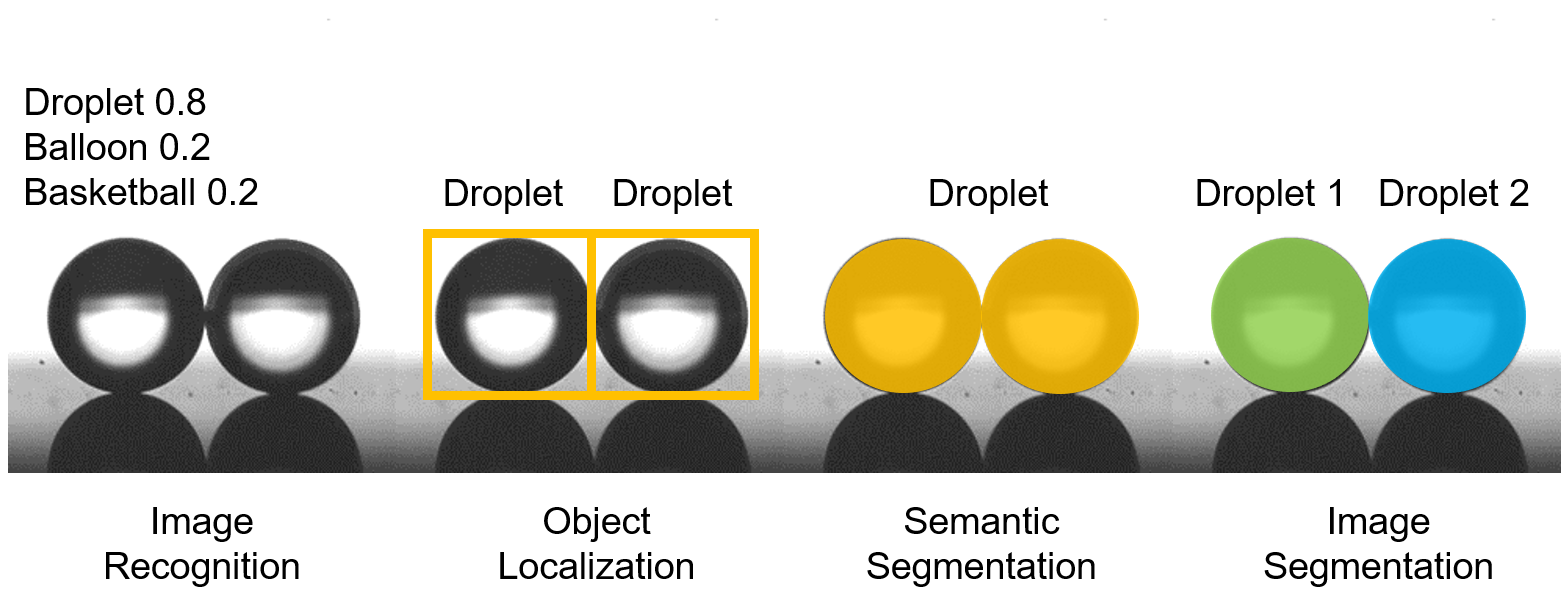
Image Recognition
Our everyday lives are full of image recognition tasks, although we may not perceive it. Our brains are just so well-developed that they effortlessly processes visual signals to differentiate objects from one another. As simplistic as it may seem, this task is actually quite a challenge for computers to imitate. From a computer’s perspective, it has to analyze pixels and patterns of an image to recognize the image as a particular object. Through machine learning processes, we can systematically teach the machine to recognize images as a certain category or label (Dog, Cat, Eagle, etc.). Since this is a simple classification problem, the machine predicts the label of the image with certain probabilities. If trained properly, the machine will predict the correct label with high probability. Note that the information we can obtain using this method is very limited.
Object Localization
Object localization works on correctly detecting an object and its specific location. The location of the object is usually labeled with bounding boxes as shown in the figure. Now, we can not only identify the presence of an object, but we gain spatial information of the object within the image. Collecting the type, rough size, and location of an object itself is an extremely useful task for many applications including autonomous driving, surveillance, and robotics. However, these methods are not suitable for applications that require detailed topological information.
Semantic Segmentation
An improvement of object localization is semantic segmentation. Semantic segmentation not only localizes objects within the image but also divides them into sets of pixels. In other words, detailed information regarding shape and size becomes available. The drawback of semantic segmentation is that it does not distinguish between objects that are of the same class. For example, if two droplets are close together as shown in the image, semantic segmentation would create a pixel-wise mask of one object labelled as a droplet.
Instance Segmentation
This is where instance segmentation becomes important. Instance segmentation is a computer vision task that generates pixel-wise masks for every object in an image. Instead of classifying two droplets as one instance, it will identify each individual droplet. Instance segmentation is an important step to extracting comprehensive image features from dynamic processes such as phase-change.
Below are a few videos that show the prediction of bubbles and droplets using a state-of-the-art instance segmentation module.
from Deep Learning Predicts Boiling Heat Transfer
Mask R-CNN
The instance segmentation module we use in our work is called Mask R-CNN.
As a brief technical description, Mask R-CNN builds on the previous semantic segmentation model, Faster R-CNN, and consists of a backbone neural network architecture Residual Learning Network (ResNet) for deep feature learning and feature extraction. Feature Pyramid Networks (FPNs) improve object representation, while Regional Proposal Networks (RPNs) and Region of Interest Align (RoIAlign) functions, which returns candidate bounding boxes. The bounding boxes are applied with bilinear interpolation to predict pixel-accurate masks. Deeper discussion on the mathematical basis of Mask R-CNN is explained in the original document.
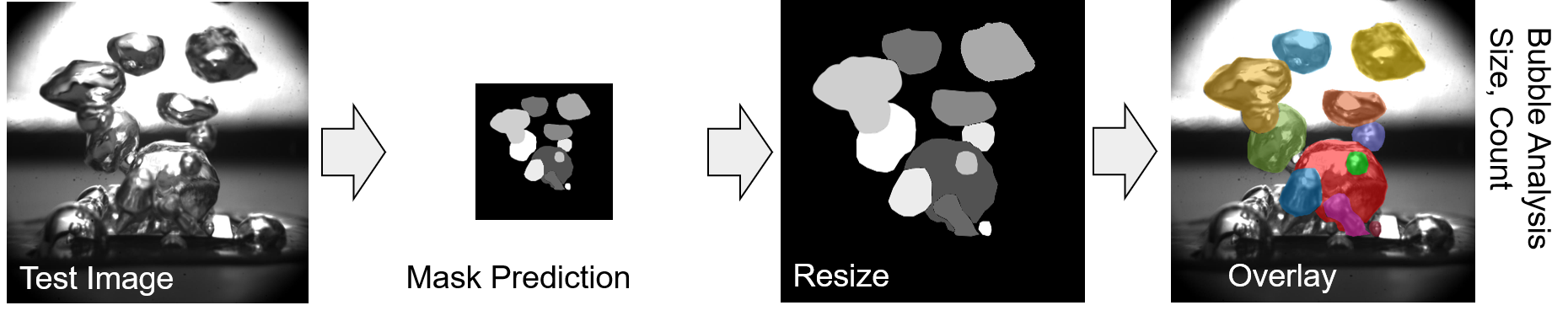
Below is a simple schematic of how Mask R-CNN works. Assuming that the model is trained, we start by plugging in the raw test image as input. The input image can be resized to speed up the mask prediction process. The predicted pixel-based masks are resized to its original size and is overlaid on the input test image for visualization. In our tutorial posts, we will learn basic steps to prepare datasets to train a custom Mask R-CNN model, which include image annotation and data augmentation.
Mask R-CNN Resources
Here is the Github repository for the implementation of Mask R-CNN on Python 3, Keras, and Tensorflow.


